
Soil is often impacted by byproducts and residual impact of industrial processes or unregulated waste disposal practices. Contaminants found in soil can include solvents, paints, oils, heavy metals, pesticides, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Contaminated soil can pose a risk to human health and the environment. It can also inhibit redevelopment of land, leaving property owners with a liability rather than an asset, which is why soil removal or environmental remediation becomes necessary.
In this post, we’ll discuss the various soil remediation techniques that can be administered on-site and why working with a professional is important.
Soil Remediation Approaches
Soil remediation objectives focus on either stabilizing, encapsulating, or removing contaminated soil from the property. There are various soil remediation technologies that can be used to meet these objectives. Remediation technologies are often classified as either “in-situ,” which means that contaminated soil is treated in place without excavation, or “ex-situ,” where soil is excavated, treated, and/or transported off-site for proper legal disposal.
Which remediation approach is best? Well, it largely depends on the severity of the contamination and which contaminants are found in the soil. Here’s a closer look at each technique:
Excavation/Disposal Removal
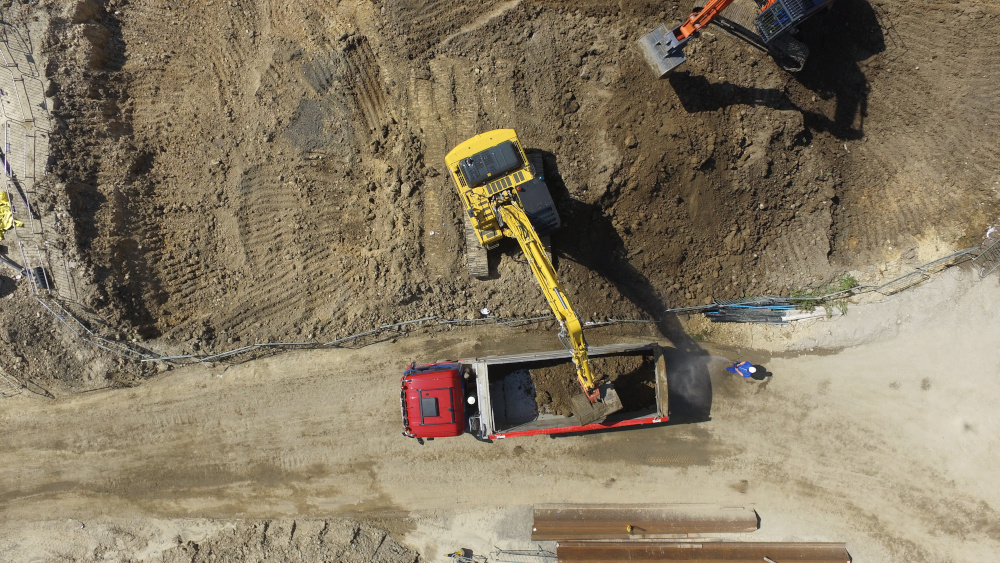

Excavation and removing contaminated soil from the site and transporting it to a facility for either treatment or disposal is one of the most common ex-situ techniques. Excavation and disposal are best suited when contamination is shallow and unsaturated. It’s also an ideal technique for contaminants that tend to be thicker, like oils or metals. Pros for excavation and disposal include certainty in removal, remediation is completed in a relatively short time frame, and engineered backfill can be designed with property redevelopment in mind. Cons of excavation and disposal include cost, impact to surrounding property and streets, and excessive fuel usage, depending on distance to disposal facilities.
Bioremediation
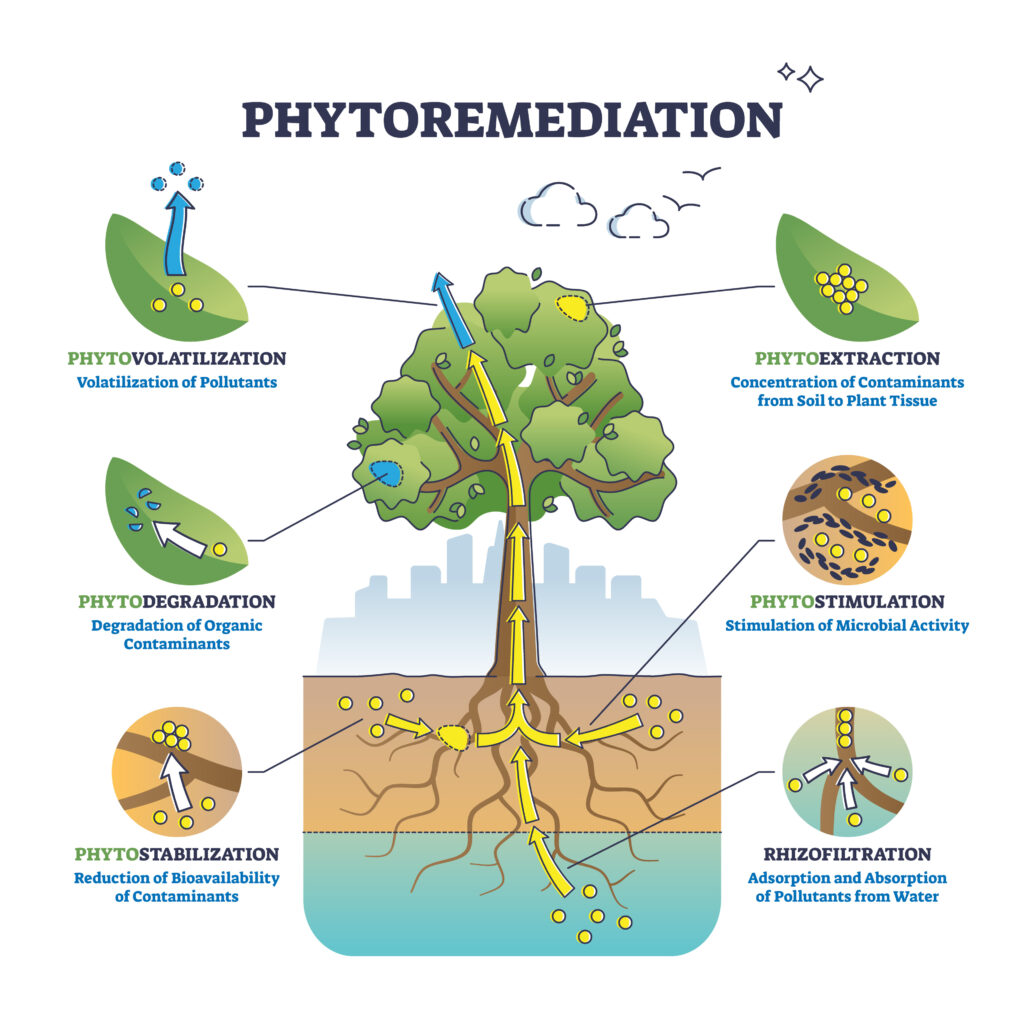
Bioremediation is an in-situ technique where microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) break down contaminant molecules into less harmful compounds. Microorganisms may be injected into the affected soil, or nutrients and oxygen are injected to feed bacteria naturally found in the soil. In-situ bio-sparging is a method where oxygen is slowly pumped into the soil using inexpensive oil-less compressors.
The pro for bioremediation includes low cost, easy implementation, and limited disturbance of the surrounding surfaces. It’s typically a cost-effective and environmentally friendly means of soil remediation. It also works best when remediating hydrocarbons, solvents, pesticides, and heavy metals.
The only downside to bioremediation is that it may take a significant time (several months or even years) to be effective, depending on the soil type and environmental conditions. It may also not be effective in remediating all contaminants.
Vapor Extraction & Air Sparging

Soil vapor extraction, or SVE, uses vacuum to remove contaminants. This fast and cost-effective process works by installing extraction wells in the areas of contaminated soil and then extracting vapors through the wells for further treatment. It’s best used on unsaturated soils with high permeability. SVE is commonly an in-situ technique and is used when remediating soil that’s been contaminated by gas, petroleum, and VOCs.
Air sparging is a similar in-situ process, but instead of extracting vapors, pressured air is injected into the soil to strip it of any VOCs. VOCs are recovered by extraction wells.
Soil Washing
Soil washing is an in-situ and ex-situ process that involves separating contaminated soil and washing it with a chemical solution to remove contaminants. It’s an ideal practice for treating soil that’s been contaminated by heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons. However, it can be expensive, and it creates a significant amount of contaminated water as a byproduct that may require further treatment before disposal.
Thermal Treatment
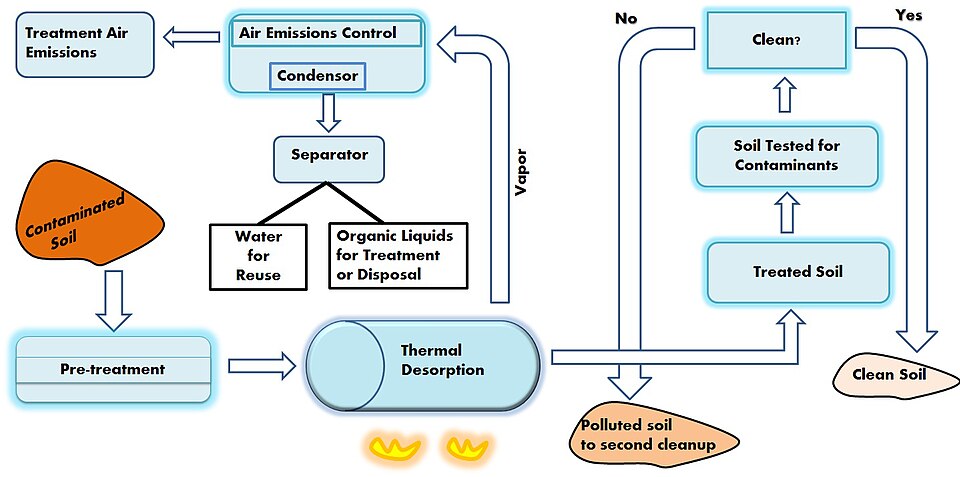
As the name implies, thermal treatment heats contaminated soil to destroy contaminants. Heat serves as the catalyst to strip or decompose contaminants, which can be removed from the subsurface using multi-phased extraction wells. Thermal treatment is an effective means of remediation, especially for eliminating organic contaminants. One downside is that the process is very energy-intensive and can be expensive. The process can be both in-situ and ex-situ.
Incineration

Incineration is a type of thermal remediation treatment that works by burning contaminated soil to destroy contaminants. Although it’s a type of thermal treatment, it’s different than typical thermal desorption because the process operates at much higher temperatures.
Incineration is ideal for treating soils that have become contaminated by chlorinated hydrocarbons, PCBs, and dioxins. In some cases, contaminated soil can be incinerated on-site. However, depending on the type of contamination, soil may need to be transferred to an off-site incinerator for processing.
Working With a Professional
If your site needs soil remediation, it’s crucial to work with a professional to ensure the best technique is used and the job is done correctly and complies with all federal and state regulations.
Regulations vary based on location. For instance, in Missouri, the Department of Natural Resources oversees soil remediation using remediation objectives (ROs) that establish the concentrations of compounds needed to be removed. Illinois has the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (IEPA), which oversees remediation with ROs that are different from Missouri. Professionals also typically comply with rules and regulations of USEPA, such as the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA), and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).
Working with a professional also ensures you’re taking proper measures to safeguard human health, protect the ecosystem, and prevent environmental damage.
Safeguard Your Environment With Help From Archview Services
Archview Services proudly helps businesses throughout the Midwest maintain safety through our comprehensive environmental remediation services, as well as our extensive EHS consulting and training opportunities.
Please complete our form or call (314) 998-4505 today to learn more about how we can help you, or visit our blog for more resources.
